Separation principle behind EUTEC™ FS filters
[Principle]Coalescence and enlargement of water droplets
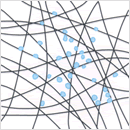
Capture of minute water droplets on microfilament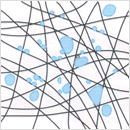
Enlargement by coalescence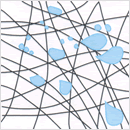
Passage of enlarged droplets through element
Finely dispersed micrometer-order droplets cannot be separated easily from oil-water mixtures by static, gravity settlement type processes. With microfilament filter, EUTEC filter elements have the capability to capture, concentrate and enlarge the minutely dispersed droplets in these kinds of turbid free fluids. Dispersed micrometer-order droplets are captured by the microfilaments of the EUTEC element and coalesce as they move along the fibers to form millimeter-order drops, which readily undergo gravity-driven stratification on emergence from the element.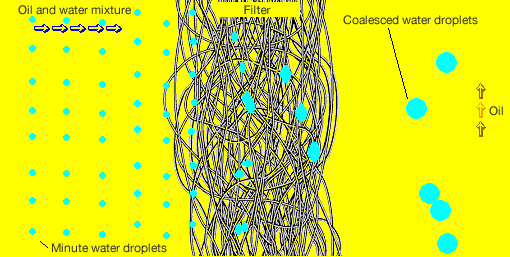
Separation mechanisms of EUTEC™ FS filters
[Mechanism]
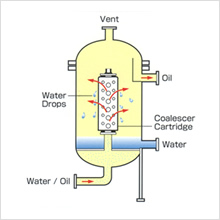
Coalescer method (one-stage separation of water from oil)
The water-oil dispersion is fed under pressure into the FS coalescer cartridge. As the dispersion passes through the coalescer element, the fine droplets of free water merge into larger drops that rapidly undergo gravity-driven stratification and collect outside the coalescer in a layer separate from the carrier liquid. For mixtures where the volume of oil is greater than that of water, the oil is extracted from an outlet in the upper portion of the vessel.
The separated free water collects in the lower portion of the vessel, and can be drained manually or via an automatic drainage valve.
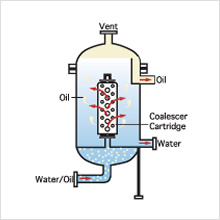
Coalescer method (one-stage separation of oil from water)
The water-oil dispersion is fed under pressure into the FS coalescer cartridge. As the dispersion passes through the coalescer element, the fine droplets of free water merge into larger drops that rapidly undergo gravity-driven stratification and collect outside the coalescer in a layer separate from the carrier liquid. For mixtures where the volume of water is greater than that of oil, the oil is extracted from an outlet in the lower portion of the vessel.
The separated oil collects in the upper portion of the vessel, and can be drained manually or via an automatic drainage valve.
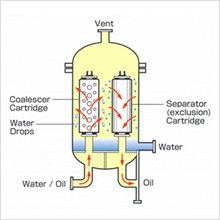
Filter-separator method (two-stage separation of water from oil)
In this method, an FS coalescer cartridge and FS exclusion-effect separator cartridge are fitted and used in tandem within the same vessel. First, the water-oil dispersion is fed under pressure into the coalescer cartridge. As the mixture passes through the coalescer, finely dispersed free water droplets coalesce and merge into larger drops, which are rapidly precipitated. In order to remove the large and intermediate-sized free water droplets that are not precipitated, the liquid is then passed through the separator cartridge. The remaining free water droplets are repelled by the surface of the filter and excluded from entry to the separator as they descend and collect in the water layer in the lower portion of the vessel. From there, the water can be drained manually or via an automatic drainage valve.














